VMware performance monitoring: Importance, benefits, and best practices for optimal VMware performance
Virtualization involves creating multiple virtual instances on a single physical server, allowing for efficient utilization of hardware resources and isolation of workloads. Businesses prefer a virtual environment as it can be tailored to meet specific security and performance requirements, and it provides numerous customization. The concept of virtualization became accessible after the emergence of VMware, a cloud computing virtualization platform for hosting complex architecture effortlessly.
VMware simplifies the workflow of and the high cost spent on maintaining physical infrastructure. It also makes data recovery easier when minor glitches occur in virtual machines (VMs). VMware is also a highly scalable tool if monitored appropriately. But like any other complex computing technology, this facet of infrastructure also has its challenges.
Monitoring VMs is different from monitoring other IT infrastructure components. It is necessary to ensure the stability of the virtual infrastructure at the host level, as VMs consume resources over a hypervisor layer. Apart from overseeing the complex nature of its setup, other challenges of a VMware environment include workload management, hardware dependencies related to VMs, complications in resource allocation, and performance degradation threats.
VMware simplifies the workflow of and the high cost spent on maintaining physical infrastructure. It also makes data recovery easier when minor glitches occur in virtual machines (VMs). VMware is also a highly scalable tool if monitored appropriately. But like any other complex computing technology, this facet of infrastructure also has its challenges.
Monitoring VMs is different from monitoring other IT infrastructure components. It is necessary to ensure the stability of the virtual infrastructure at the host level, as VMs consume resources over a hypervisor layer. Apart from overseeing the complex nature of its setup, other challenges of a VMware environment include workload management, hardware dependencies related to VMs, complications in resource allocation, and performance degradation threats.
What is VMware monitoring, and why do you need it?
VMware monitoring aids in ensuring all your VMware vSphere components are up and running. It manages all the attributes of your VMware environment and helps you optimize its function according to your needs. A VMware monitoring tool pinpoints and helps resolve the factors slowing down your VMs. Managing a VMware vSphere environment with a tool designed to ease your virtualization experience can help reduce performance degradation, enhance productivity, minimize downtime, and ensure all your business goals and requirements are aligned.
As much as monitoring VMware is essential, it is also crucial that your VMware infrastructure is monitored for the correct parameters. The complexity of a vast virtual setup is daunting. Still, you can overcome the challenges hindering its performance with the proper practices.
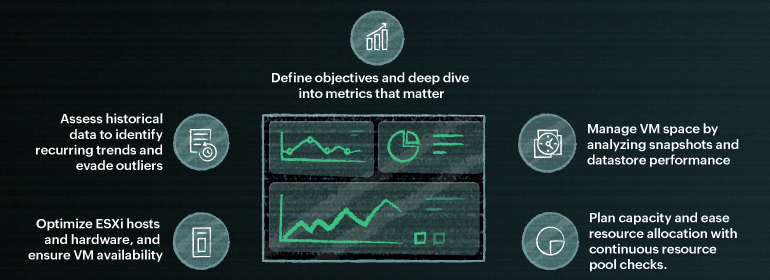
Here are a few mindful practices to administer for your VMware's healthy functioning.
Here are a few mindful practices to administer for your VMware's healthy functioning.
1) Define objectives and deep dive into metrics that matter
Keeping track of all metrics can be confounding. Instead, prioritize your needs and monitor the parameters of the set goal. If a bank functioning on a VMware architecture is worried about response time lags during peak hours, monitoring metrics related to CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O latency, and transaction response time will help it avert potential setbacks.

To prioritize your objectives, defining a baseline is essential. Determining the threshold for normal will ease identification of any deviations, help isolate the specific metric, and administer necessary remediation. Once a baseline is set, any anomaly can be flagged and notifications sent through preferred communication channels.

To prioritize your objectives, defining a baseline is essential. Determining the threshold for normal will ease identification of any deviations, help isolate the specific metric, and administer necessary remediation. Once a baseline is set, any anomaly can be flagged and notifications sent through preferred communication channels.
2) Optimize ESXi hosts and hardware, and ensure VM availability
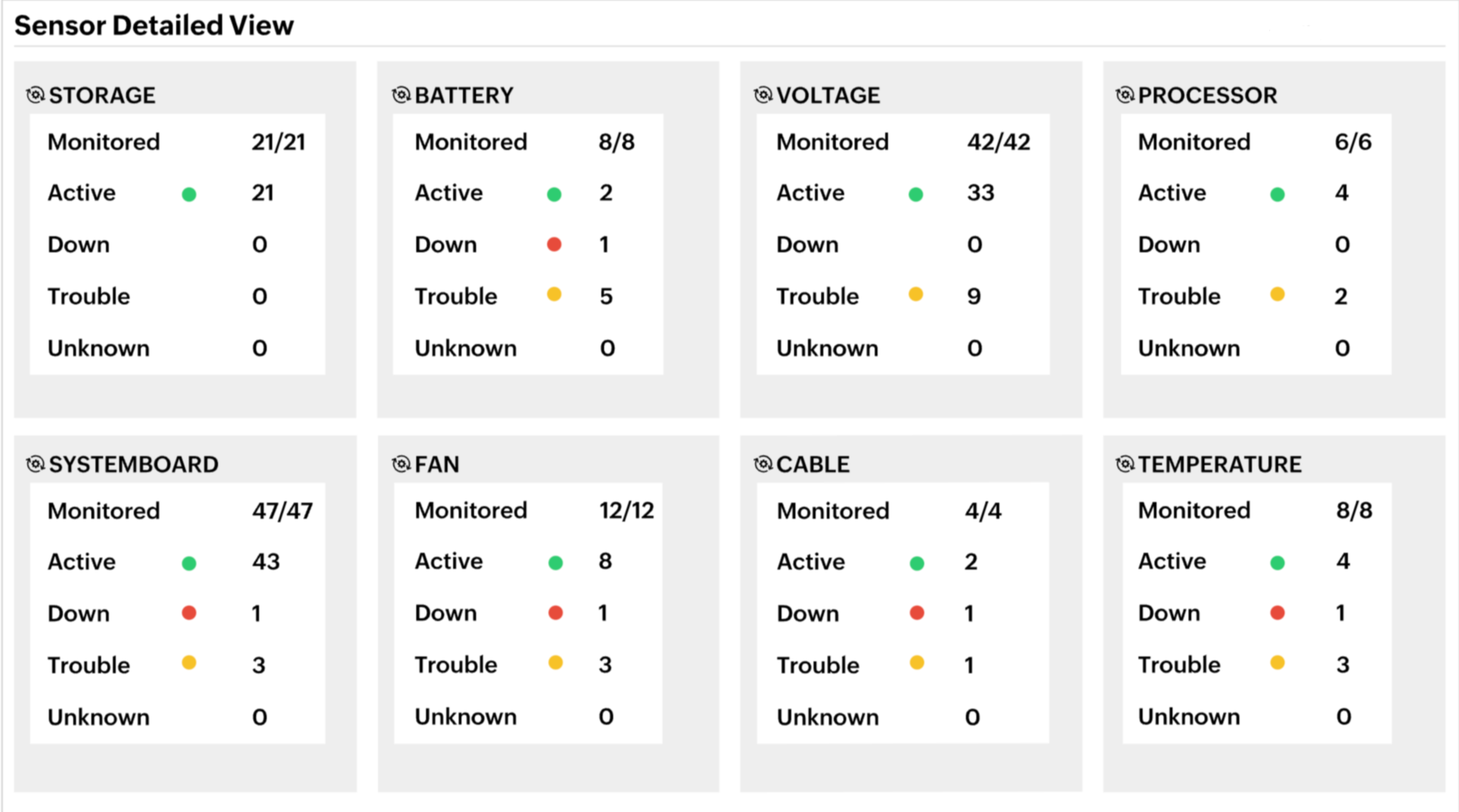
ESXi is a pivotal component of the VMware virtual environment, containing all its underlying resources. Faulty ESXi host health might lead to degradation in VM performance. You should keep a close eye on ESXi hosts' critical metrics, like CPU, memory, disk, and network components, never letting your VMs run low on resources. Along with the host, it's also important to monitor the health of all your hardware components, including the fan, temperature, voltage, power, storage, battery, and Watchdog, to ensure your VMs are available around the clock without any impediment in performance.

Note: How can temperature and fan speed help in ensuring VM performance?
High temperatures can lead to thermal throttling; in most cases, hardware components lower their pace to prevent potential damage. In turn, this impacts the performance of VMs running on the affected hardware. Monitoring temperature and fan speed to ensure proper cooling helps maintain optimal performance levels for the hardware and the VMs.
3) Manage VM space by analyzing snapshots and datastore performance
Snapshots are instantaneous save points taken of the server at a particular time for temporary use to help the server restore to the same point in case of an issue. But, over time, these snapshots occupy space and hoard the resources allotted for VMs, resulting in storage issues. In order to free up space, it is essential to monitor orphaned, untracked, and aged snapshots. Clearing these snapshots will make datastores more efficient.
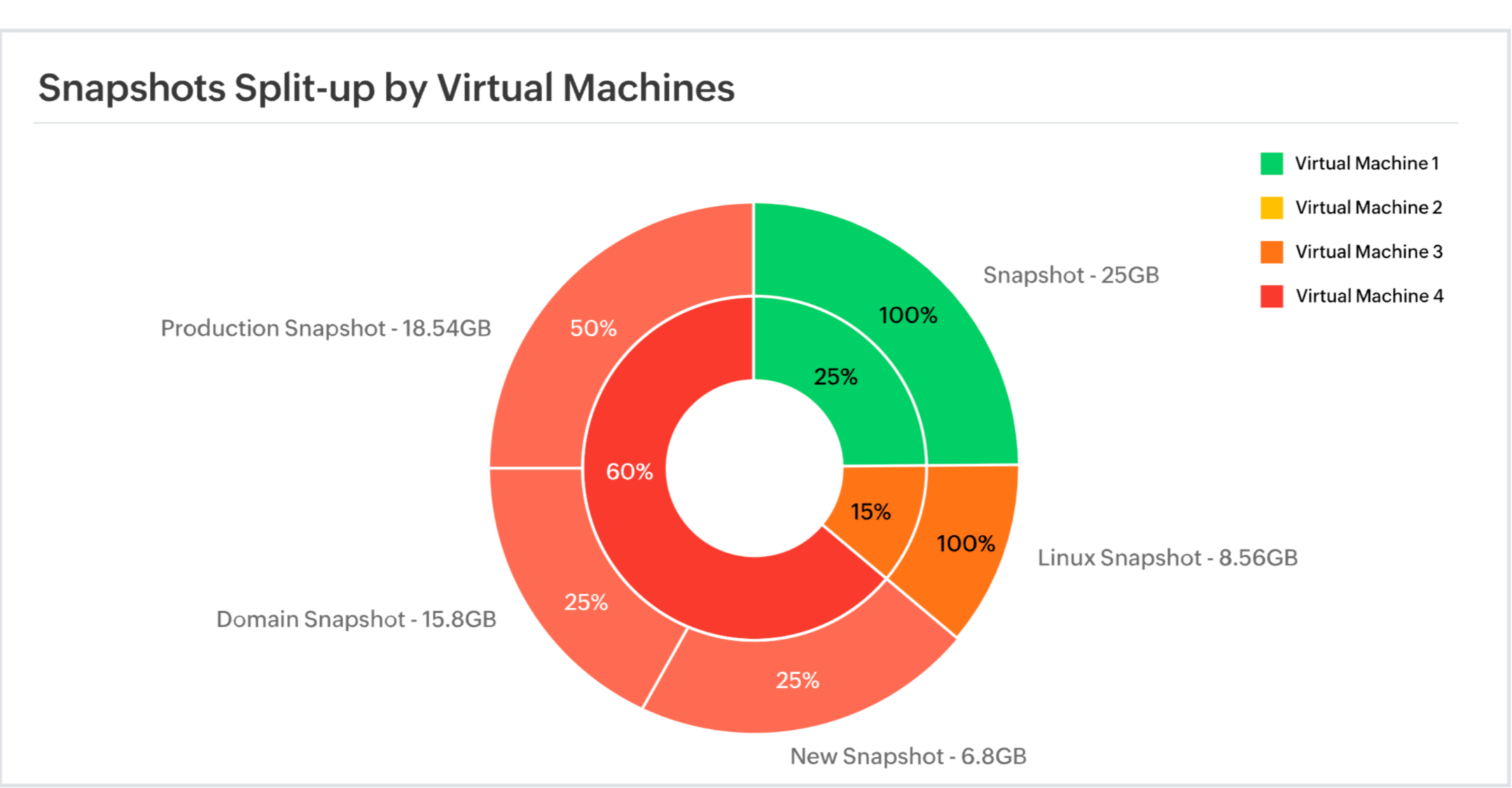
In a VMware architecture, the datastore is the storage entity; it manages the space for available, occupied, and allocated resources. Evaluating datastore performance can help pinpoint the VMs exhausting the resources, resulting in resource contention and avoiding productivity issues.
4) Plan capacity and ease resource allocation with continuous resource pool checks
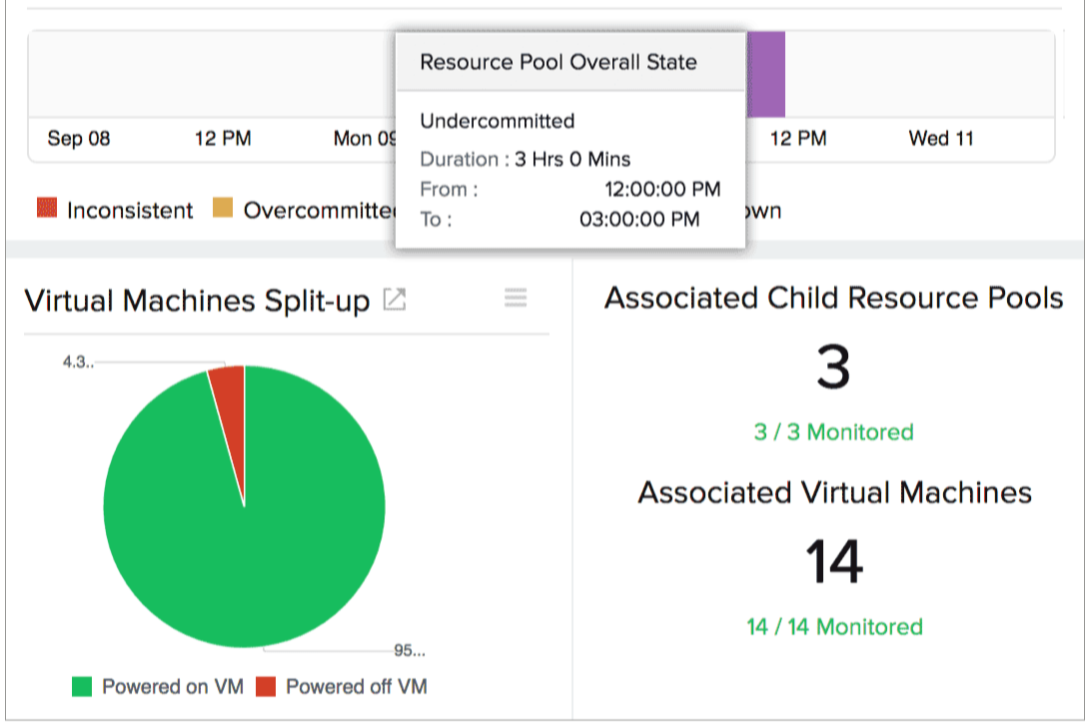
Managing your resources and planning your capacity go hand in hand. Just as the datastore is the storage entity, the resource pool is the resource allocator. Capacity planning for a VM marks the foundation of any virtual operation. Insights into the resource pool can help cross-check the adequate distribution of resources to avoid over- or under-provisioning. Though VMs with low storage can be scaled up, VMs amassing space can lead to resource contention. Monitoring critical resource pool metrics like CPU and memory utilization, as well as their reservations, limits, and share value, can help you prioritize resource allocation based on resource utilization patterns and workload behavior and requirements.

For example, an IT team has production, development, and testing workloads running on a VMware setup. Monitoring the resource pool can help them prioritize and fine-tune resource shares and increase CPU and memory resources to the production resource pool to ensure that critical production applications are always up and running.
5) Assess historical data to identify recurring trends and evade outliers
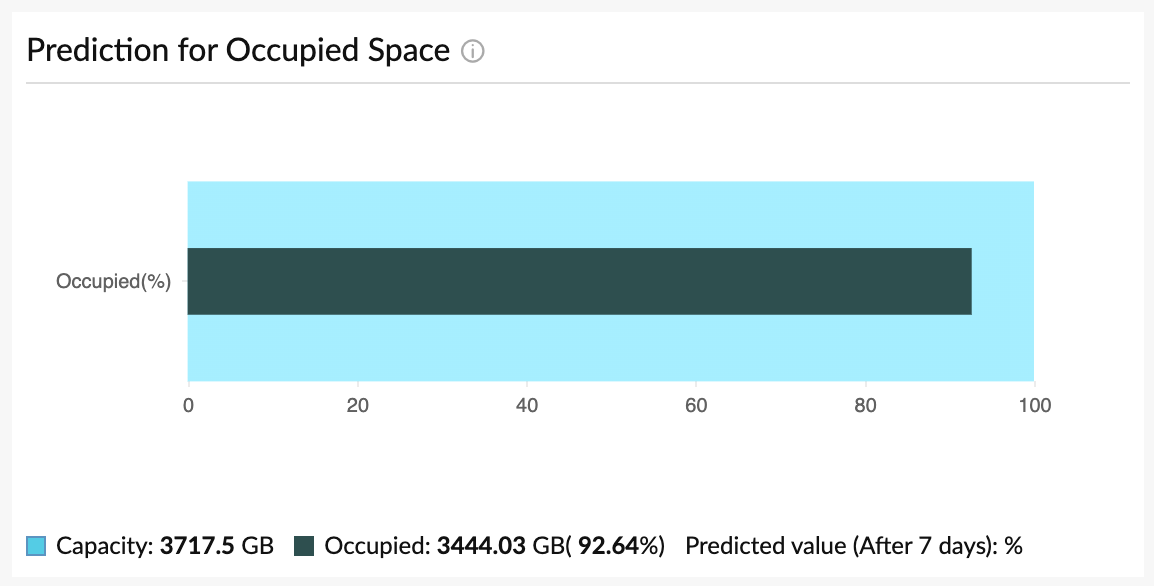
Receiving alerts and getting notified about your VMs' anomalous performance is necessary. Observing the trends and patterns over time is also essential to formulate strategies and decide on the best course of action for maintaining VMware health. Historical reports mitigate performance degradation by providing context from past data to avoid unexpected performance bottlenecks. Generate reports capturing various metrics to strategize plans, optimize infrastructure, and manage complex systems like virtualized environments. You should utilize reports even when all the monitors work fine to ensure all your monitoring parameters meet your changing priorities and requirements.
Conclusion
The main takeaway of this blog is that when a diligent monitoring plan for your VMware infrastructure is implemented, along with the recommended set of best practices facilitated by a monitoring tool like Site24x7, it can save the organization from critical holdbacks.
Site24x7 monitors your entire VMware vSphere environment in various hierarchical levels and reduces workflow tedium in a single click, without drilling a hole in your pocket. You can also explore granular details of VMware components, like vCenter or hypervisors such as ESX/ESXi hosts, clusters, datastores, resource pools, and snapshots. With features like intuitive dashboards, IT automation, AI-based insights, and numerous third-party integrations, you can reduce the gap between knowing about and resolving a problem. Try Site24x7 now.
Comments (0)