Why HTTPS is important for your website security
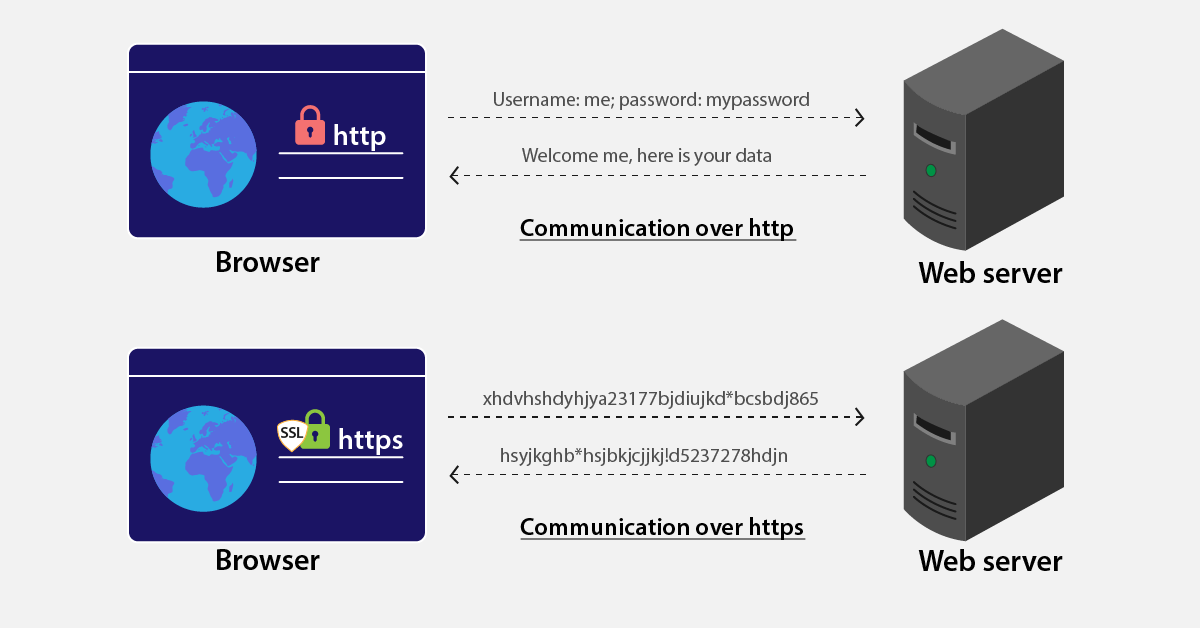
HTTP, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a communication protocol used by your browser to connect to the web server of the site you're looking for. When HTTP data transfer between the browser and the web server is shared via unencrypted hypertext, anybody connected to your network can intercept the data you're transferring. To combat this, it's best to switch to HTTPS, the more secure extension of HTTP.
You can't verify data integrity with HTTP
Without the S, which stands for secure in HTTPS, your connection is prone to threats like man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, where an attacker can intercept the communication between two parties in a network and taint it by injecting their own messages. With the lack of endpoint authentication, an attacker who has access to an unencrypted Wi-Fi network can implant themselves as the MITM. Passwords and credit card numbers shared over a compromised network are also easily stolen by eavesdroppers and phishers.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
In 2018, Google started flagging websites that do not have HTTPS as insecure, prior to which most websites operated on HTTP. Any static website that does not collect user information in any form might still operate on HTTP today.
The insecurity of HTTP can be overcome by switching to HTTPS, which encrypts communication and makes it difficult for attackers to intercept the network. For example, when you're entering in your credit card details over a secured network, an attacker will only see random, meaningless text.
To implement HTTPS for your website, you must:
1. Purchase an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
2. Configure hosting with the SSL certificate.
3. Redirect all internal links from HTTP to HTTPS.
4. Implement 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS.
5. If you're using a content delivery network (CDN), update its SSL settings.
Once you're done, your site will look like this:
Build trust with SSL
When a site has an SSL certificate, the browser establishes a connection with the web server using an SSL handshake; this means that a private key, a public key, and a session key are required to decrypt the connection request and establish it.
HTTPS makes your website more secure, and imparts trust to the users visiting your site. Seeing that a trusted CA has issued the SSL certificate affirms that your website is legitimate, and acts as an assurance for data integrity.
HTTPS is mandated by Google
As of 2014, Google began recognizing that sites that have enabled HTTPS rank better than those without. Google's search engine optimization (SEO) policy states that HTTPS sites receive a small ranking boost, but don't expect a visible change. Though it's a low ranking factor, failure to make the switch can leave you vulnerable to sudden changes in Google's ranking algorithm.
Ensure that the HTTPS you've set up stays secure
HTTPS isn't foolproof. While it does add a strong layer of security, HTTPS-enabled websites are still prone to cyberattacks. For example, SSL Stripping circumvents the SSL's security by downgrading HTTPS to HTTP, and untrusted and forged CAs pose a threat just like expired certificate, affecting your overall SEO rankings. You can overcome these challenges with an SSL/TLS monitoring tool that detects and warns webmasters of a certificate expiry and certificate tampering.
Is monitoring SSL certificates significant?
On May 30, 2020, when the AddTrust External CA Root expired, many services were affected, including select streaming channels of popular streaming device Roku. Stripe, a payment processor, also faced issues where the webhook delivery failed for some users.
While it may seem like keeping track of a certificate's expiry is easy, keeping track of multiple certificates is quite tedious, especially for large organizations. There's more to SSL certificate monitoring than just tracking its expiry; possible malware tampering or a certificate revocation could also occur, among other issues. Monitoring tools make it easier for webmasters and site owners to keep an eye on the health of SSL certificates.
Be aware of CA blacklisting
Site24x7, a comprehensive web monitoring tool, performs periodic checks to verify the validity of the SSL certificates. Checks via Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) and certificate revocation lists (CRLs) are made to identify revoked certificates, blacklisted checks weed out a potential blacklisted CAs, and SHA-1 Fingerprint thresholds detect potential certificate tampering and alerts you instantly.