Experienced IT professionals know that not all server performance issues announce themselves with loud crashes or overt failures. Often, the most dangerous threats arrive quietly. They slip past routine checks, degrade performance insidiously, and ultimately bring critical business services to a crawl. Understanding and monitoring these threats are essential to safeguarding server stability, optimizing resource utilization, and delivering an uninterrupted user experience.
Memory leaks
What is a memory leak?
A memory leak is when memory is claimed by an application (via allocation) but is not released after use. This stranded memory accumulates with each transaction, user session, or job, gradually depleting the available RAM. In simple terms, it is like a factory where each completed product still occupies a workspace, eventually leaving no room for new production.
Memory leaks occur when an application or process allocates memory but fails to release it back to the system once it is no longer needed. Like a tap left running, memory slowly drains away, reducing what is available for the rest of the system until the server eventually grinds to a halt.
Common causes
- Unclosed connections or file handles (databases, sockets, files, etc.)
- Improper object disposal in managed languages (Java, C, Python, etc.)
- Long-running processes with poor resource hygiene
- Third-party library bugs or misconfigurations
- Garbage collection issues―in Java, .NET, or Python, persistent object references keeping memory alive longer than intended
Symptoms to watch for
- A gradual, linear, or stepped increase in memory utilization over time
- Swapping memory―the system swapping RAM contents to the disk, drastically increasing latency
- Out of memory (OOM) errors and application crashes
- General system sluggishness or unresponsiveness
How can you prevent memory leaks?
- Tracking memory usage trends: Continuous monitoring and retention of historical data make it possible to spot slow memory growth that could otherwise evade notice.
- Per-process memory monitoring: Pinpoint which server process is responsible. For example, is your JVM-based app, a background daemon, or a database subsystem leaking memory?
- Alerting based on thresholds: Intelligent monitoring tools allow you to set custom thresholds not just for absolute memory use but for consistency of upward trends, helping you catch leaks before OOM failures occur.
- Heap dumps and snapshots: For languages like Java or .NET, capturing heap dumps when suspicious activity is detected gives you deeper forensic details on which object types and collections are swelling over time.
CPU bottlenecks
What is a CPU bottleneck?
A CPU bottleneck arises when the processor cannot keep pace with the volume or complexity of tasks it must perform, even though other system resources (like memory, disk, or network resources) are available. The result is that tasks pile up while waiting for CPU attention, leading to a chain reaction of delays across applications and related infrastructure.
CPU bottlenecks happen when the CPU becomes the limiting factor in system performance. Even if disk, network, and memory resources are available, an overloaded CPU can prevent the system from processing tasks efficiently, causing severe slowdowns or intermittent lag.
Common causes for CPU bottlenecks
- Inefficient algorithms or poorly optimized code blocks
- Infinite loops or runaway background jobs
- High concurrency operations that lead to too many threads or processes competing simultaneously
- I/O wait states and resource contention
- Single-threaded applications running on multi-core servers, failing to utilize available cores
- Resource contention from misconfigured middleware, batch jobs, or API endpoints
CPU bottleneck indicators
Even if you do not suspect CPU bottlenecks, keep an eye on these symptoms:
- Sustained high CPU utilization (over 85% or near 100%)
- Slow application response times, timeouts, or periodic performance drops
- High load averages (see load averages explained), especially when queued processes outnumber the core count
- Run queue growth―more processes waiting to be scheduled on the CPU
- High context switch rates―excessive task switching, signaling thread contention or lock contention
- Processes stuck in a runnable state for extended periods
How to detect CPU bottlenecks
- Overall CPU utilization: Track the total and per-core usage to spot when system-wide CPU saturation occurs.
- Per-process CPU utilization: Zero in on exactly which process, process ID, or instance is responsible for spikes.
- Context switching rates: Identify contention caused by excessive multithreading or lock contention.
- Load averages: Understand the load average (e.g., in Linux), which indicates how many processes are waiting for CPU time. A load average above the total core count is generally a sign of CPU pressure.
- CPU run queue monitoring: Persistent growth signals that the CPU is the constraining factor.
- Thread-level monitoring: In Java, .NET, and other environments, track activity and contention at the thread level for root cause analysis.
Consequences of unchecked leaks and bottlenecks
- Degraded user experiences: Slow-loading applications annoy and drive away users.
- Increased infrastructure costs: Band-Aid solutions like adding more RAM or CPU capacity may mask the root issue without resolving it.
- Application instability and downtime: Persistent errors can result in costly outages.
- Increased operational risks: Undiagnosed leaks and bottlenecks can be exploited to exhaust resources, increasing security vulnerabilities.
Diagnosing the invisible
Site24x7's server monitoring provides a comprehensive toolkit for memory leak monitoring, CPU bottleneck detection, and ongoing server troubleshooting with these key capabilities:
Granular process monitoring
- Track CPU usage, memory utilization, and thread and handle counts per process.
- View historical charts to identify resource leaks and trends.

Historical data and baselines
- Visualize weeks or months of resource utilization to identify slow leaks or creeping CPU saturation.
- Detect deviations from established baselines using anomaly detection.
Customizable thresholds and alerts
- Set system-wide or process-specific alerts for high memory usage, high CPU usage, escalating thread counts, and more.
- Use escalation policies to notify the right teams before minor issues become critical.
Integrated log management
- Correlate OOM events, application exceptions, and system messages with performance metrics for faster root cause analysis.

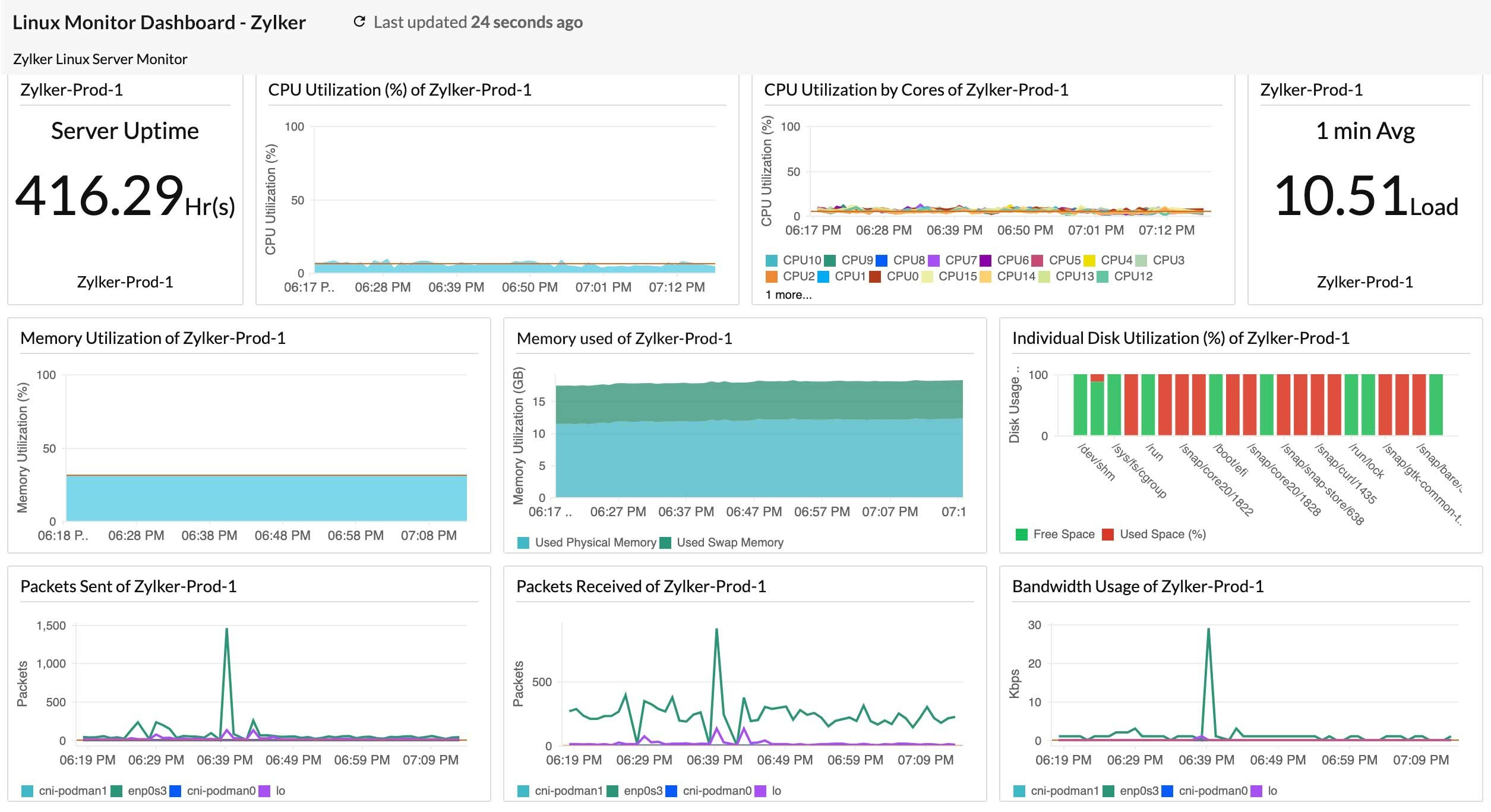
A unified dashboard view
- See CPU, memory, disk, and application performance monitoring metrics on a single pane.
- Quickly correlate trends and spot the interplay between system resources and application health.
AI-powered anomaly detection
- Automatically learn the normal patterns of utilization and flag suspicious deviations. This helps you catch issues not covered by static thresholds.
With intricate process monitoring, you can move from suspicion to action in minutes.
Best practices
With the practices listed below, you can fortify your IT infrastructure against performance degradation:
- Identify inefficient memory management or CPU-intensive code during development.
- Detect leaks or bottlenecks before deployment by simulating the production load.
- Always close connections, handle errors gracefully, and leverage language-specific best practices (e.g., try-with-resources in Java).
- Ensure applications are provisioned with appropriate CPU and memory resources based on monitored usage patterns.
- Use modern tools for 24/7 alerting and remediation, not just periodic manual checks.
From crises to control
Memory leaks and CPU bottlenecks are subtle, complex, and often business-critical server performance issues. They hide in plain sight, undermining your application reliability and infrastructure ROI. Yet with proactive monitoring, deep process analysis, and intelligent alerting, these silent killers can be swiftly exposed, diagnosed, and resolved.
Transform your IT operations management by making comprehensive, data-driven monitoring the foundation of your server health. Don’t wait for the next OOM or CPU saturation crisis. Leverage Site24x7 to reveal and remediate the hidden causes of your slowdowns before your end users notice.