Redis is known for its blazing speed, low latency, and lightweight memory footprint. But even the fastest in-memory databases can run into performance bottlenecks—especially when memory is not managed well. One of the subtle yet significant culprits behind deteriorating Redis performance is memory fragmentation. In this article, we’ll explore what it is, why it matters, and how monitoring it with Site24x7 can help you stay ahead of the curve.
What is memory fragmentation in Redis?
Memory fragmentation occurs when the memory allocator (like jemalloc, used by default in Redis) cannot reuse freed-up memory efficiently. As Redis adds and removes keys, especially with variable-sized data, the allocator breaks memory into chunks of different sizes. Over time, this leads to small, unusable gaps scattered across memory—even though your application might not be using that much data.
In simpler terms, fragmentation means your system appears to use more memory than it actually needs.
Why early detection of fragmentation matters
While Redis does its job in the background, high memory fragmentation can:
- Increase memory usage unnecessarily
- Slow down memory-intensive operations
- Trigger key evictions even when plenty of memory should be available
- Lead to performance issues and higher infrastructure costs—especially in cloud environments
That’s why early detection and prevention of fragmentation is key in maintaining Redis performance.
Key metrics to monitor in Redis
Using Site24x7, you can track dozens of Redis performance metrics, but let’s zoom in on those that directly or indirectly relate to memory fragmentation.
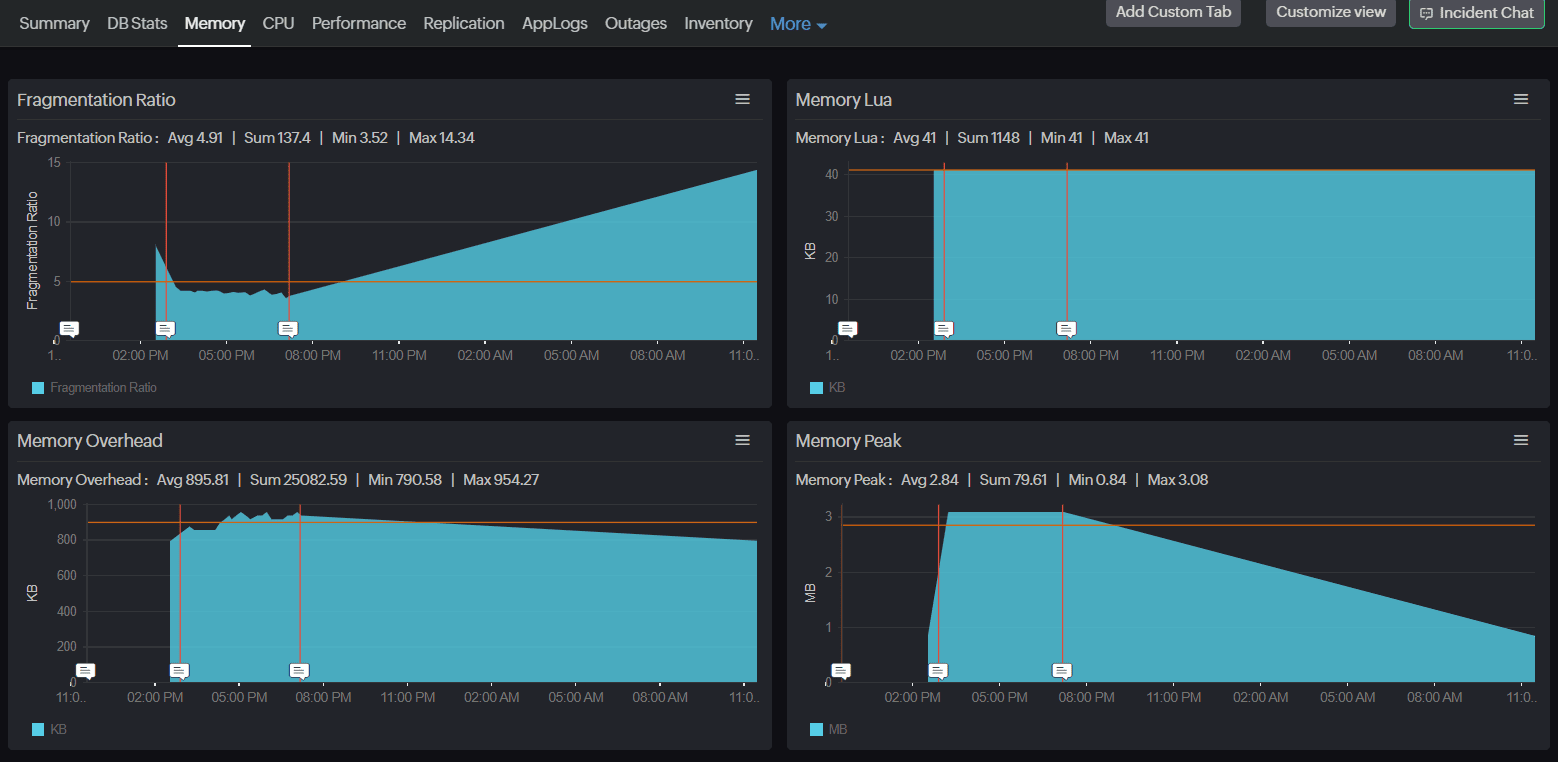
1. Fragmentation Ratio
This is the primary metric to keep an eye on. It is calculated as:
Memory RSS / Used Memory
- Memory RSS: The memory Redis has allocated, as reported by the operating system.
- Used Memory: The memory actually used by Redis data.
A fragmentation ratio close to 1.0 is ideal. Anything significantly higher (for example, 1.5 or above) indicates wasted memory due to fragmentation.
2. Used Memory and Memory Overhead
Tracking used memory over time alongside memory overhead can reveal how Redis's internal structures are growing. Overhead includes everything from key metadata to buffers.
3. Memory Peak and Memory Startup
- Memory Peak: Peak memory used since Redis started.
- Memory Startup: Memory used during initial load.A rising gap between these two could hint at unoptimized memory usage patterns over time.
4. Evicted Keys and Expired Keys
While these don't directly signal fragmentation, sudden spikes in evictions, especially when fragmentation ratio is high, could mean Redis is freeing keys not because of real memory pressure, but because the allocator can't reclaim memory efficiently.
Redis memory optimization: The role of active defragmentation
Redis introduced active defragmentation to automatically clean up and optimize memory usage when fragmentation crosses certain thresholds. It helps reduce memory fragmentation by reallocating scattered memory blocks into contiguous chunks while the server is running. It activates only when certain thresholds are met, such as high fragmentation levels and available idle CPU. The process is lightweight, non-blocking, and runs in short time slices to avoid performance impact.
While it provides valuable cleanup, active defrag isn’t a complete solution. Manual strategies—like optimizing data structures or reducing key churn—often have a greater long-term effect. Active defrag works best as a background maintenance tool, especially when paired with proactive monitoring through solutions.
This is where Site24x7 assists with its Redis monitoring plugin. It helps detect memory fragmentation early by tracking key metrics like fragmentation ratio and active defrag activity. With custom alerts and visual trends, it enables proactive tuning and timely interventions before fragmentation impacts performance.
Key metrics you should watch
- Active Defrag Hits: Number of values successfully reallocated by the defragmentation process. A higher number means defragmentation is doing its job.
- Active Defrag Key Hits: Number of keys that were successfully defragmented.
- Active Defrag Misses: Number of value reallocations that failed or were aborted.
- Active Defrag Key Misses: Number of keys skipped or untouched during the process.
- Active Defrag Running: Indicates if defragmentation is currently in progress.
By watching these metrics, you can confirm whether Redis is effectively managing its memory and taking corrective action in real time.
Strategies to prevent or reduce fragmentation
Even with monitoring in place, prevention is always better than cure. Here’s how you can reduce the risk of memory fragmentation in your Redis instance:
1. Enable active defragmentation
Make sure the activedefrag setting is enabled in your Redis config:
bash
activedefrag yes
Redis versions 4.0 and later support this feature. You can also tune thresholds like active-defrag-threshold-lower and active-defrag-cycle-min for more control.
2. Use efficient data structures
Some data types are more memory-friendly than others. For example:
- Use hashes to group similar keys under one namespace
- Avoid creating massive individual keys with large values
Small design changes can lead to more compact memory layouts and less fragmentation.
3. Set a realistic maxmemory limit
Redis supports setting a maxmemory cap, which, when combined with the right eviction policy (allkeys-lru, volatile-lru, etc.), helps maintain control over memory usage.
But be careful—if fragmentation is high, Redis might hit the maxmemory limit even if there’s plenty of used memory available. Monitoring Evicted Keys along with the fragmentation ratio can help avoid unnecessary key evictions.
4. Monitor trends continuously
Fragmentation builds up over time. Using Site24x7’s Redis plugin, you can:
- Set custom alerts for fragmentation ratio, defrag misses, or memory usage
- Visualize long-term trends with built-in dashboards
- Correlate fragmentation metrics with operational metrics like:
- Ops/Sec (operations per second)
- Blocked Clients
- CPU User and CPU Sys
This kind of holistic visibility is key to catching inefficiencies early and optimizing performance.
Redis monitoring made easy with Site24x7
Memory fragmentation is one of those issues that quietly chips away at Redis performance—until one day, it blows up into a serious problem. But with the right strategies and real-time monitoring in place, it doesn’t have to be a mystery.
Site24x7’s Redis monitoring plugin covers all essential metrics to give you a full picture of your Redis instance—from memory usage and performance to defragmentation stats and network traffic.
With automated alerts, visual dashboards, and support for custom thresholds, Site24x7 helps teams detect memory fragmentation issues early and fix them before they lead to downtime or degraded performance. Start monitoring Redis memory health today and prevent performance issues before they begin.